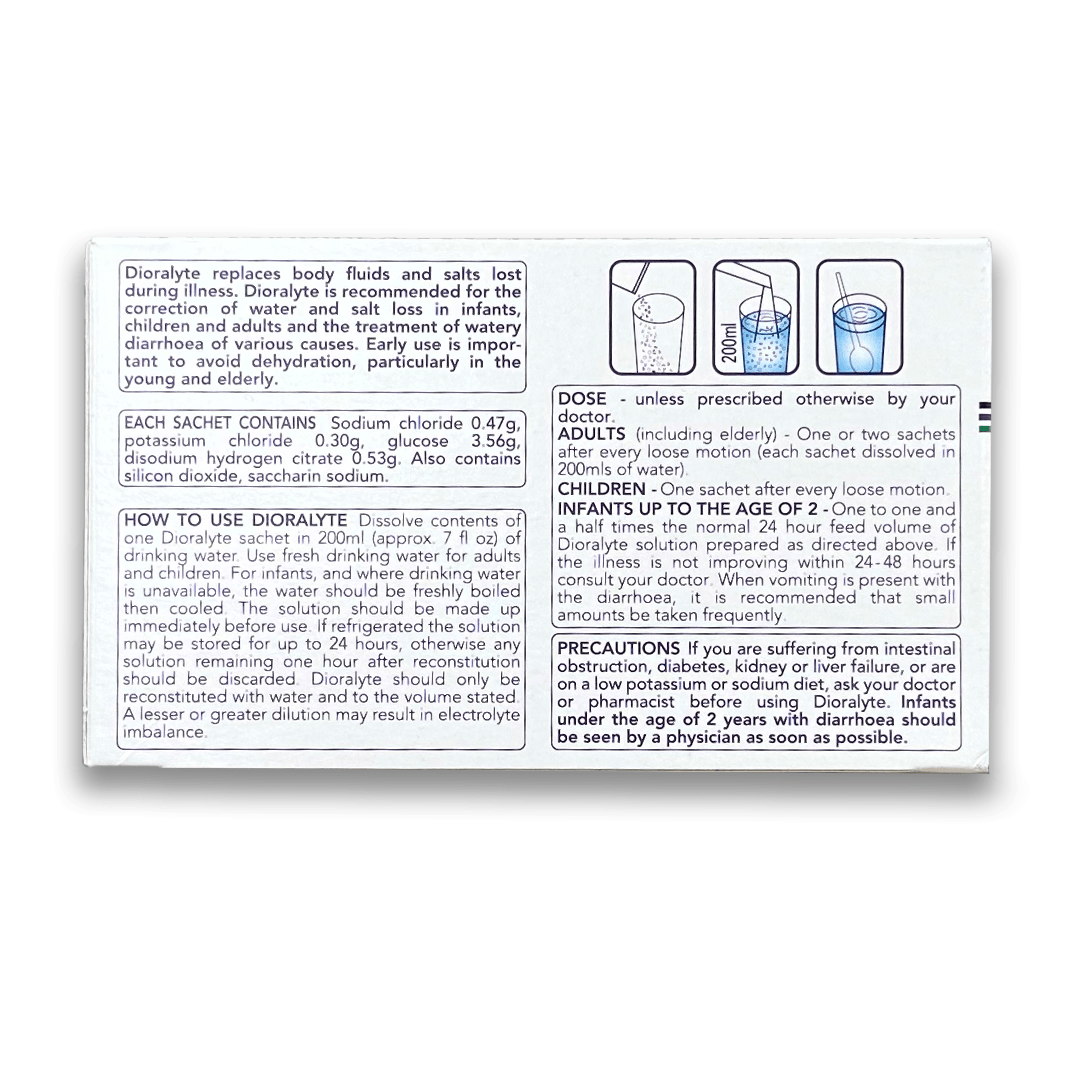
Preventing diarrhea involves adopting healthy habits and precautions to minimize the risk of infection and digestive disturbances:
- Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially before eating and after using the restroom, to prevent the spread of infections.
Food Safety: Consume clean, properly cooked foods, and avoid eating raw or undercooked meats, seafood, and eggs.
- Water Quality: Drink safe, bottled or purified water when traveling to areas with questionable water quality.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques to support digestive health.
Vaccinations: Some travel destinations may require specific vaccinations to reduce the risk of infections that cause diarrhea.
In conclusion, diarrhea is a common digestive symptom that can be caused by various factors, including infections, dietary triggers, and underlying conditions. Proper hydration, dietary adjustments, and appropriate treatment measures can help alleviate symptoms and promote recovery. Maintaining good hygiene, food safety practices, and stress management techniques can contribute to reducing the risk of diarrhea and maintaining optimal digestive well-being. If diarrhea is persistent, severe, or accompanied by additional concerning symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended for proper evaluation and guidance.